In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the battle between defenders and attackers is relentless; as technology advances, so do the tactics of cybercriminals.
At the FBI Atlanta Cyber Threat Summit in July, Director Christopher Wray warned that cybercriminals are weaponizing Artificial Intelligence (AI), and it is due to get worse as machine-learning models grow more sophisticated.
While AI is one of the most cutting-edge tools available, cybercriminals are harnessing its powers for their own nefarious purposes.
To stay ahead of those threats, cybersecurity professionals are turning to AI, too.
“AI is a game-changer in cybersecurity, enabling organizations to detect and automatically respond to threats at a pace previously not possible,” said 360 Advanced Sr. Practice Director Brad Lyons.
Let’s explore how AI is being used by both cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals, the risks it poses, and how it can enhance threat detection and response.
The Rise of AI in Cybersecurity
AI, with its ability to process vast quantities of data at lightning speed and make humanlike decisions, using various mathematical algorithms and optimization techniques, neural networks, machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and big data, is quickly becoming transformational to the world of cybersecurity.
Four ways AI is being leveraged by cybersecurity professionals to protect digital assets:
- Advanced Threat Detection – One of the most critical roles AI plays in cybersecurity is detecting previously unknown threats. Traditional signature-based antivirus solutions struggle to keep up with the constant stream of new malware.
AI-powered tools can analyze the behavior of files and applications to identify suspicious activities, even without a known signature “AI-driven threat detection is like having a digital sentinel that can spot even the subtlest signs of malicious activity,” Lyons said.
- Behavioral Analysis – AI systems can monitor user and network behavior to identify anomalies. By establishing a baseline of “normal” behavior, AI can quickly flag any deviations, potentially indicating a cyber threat. This allows for real-time threat detection, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced cyber landscape.
“AI’s ability to analyze behavioral patterns in real-time allows us to pinpoint suspicious activity before it escalates into a full-blown attack,” said 360 Advanced’s Associate Practice Director David Brosi.
- Automated Incident Response – When a security incident occurs, time is of the essence.AI can automate incident response by isolating affected systems, quarantining malicious files, and even initiating countermeasures to halt an attack in progress.AI-driven automated incident response helps business combat bad actors. It allows them to contain threats swiftly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Security Analytics – With the ability to analyze massive datasets, AI can provide security professionals with valuable insights into the ever-changing threat landscape. This information allows for better decision-making and resource allocation.AI’s analytical powers are indispensable for making sense of the vast amount of data generated in modern cybersecurity operations.With the exponential growth of digital information and the constantly evolving threat landscape, relying solely on human analysis is no longer feasible.AI not only helps process the deluge of data but also uncovers hidden patterns and anomalies that would otherwise remain undetected through purely human analysis.
The Dark Side: How Cybercriminals Harness AI
While AI is a powerful tool in the hands of cybersecurity defenders, it is equally potent when wielded by cybercriminals.
Here’s how malicious actors are using AI for their nefarious purposes:
Automated Attacks
“AI-driven automated attacks are the cyber equivalent of a relentless and ruthless army,” Brosi said. “Unfortunately, they’re capable of causing immense disruption, leading to business downtime, fines, penalties—it is a nightmare.”
AI-driven bots can carry out large-scale attacks, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, with minimal human intervention. These automated attacks overwhelm target systems and can render them inaccessible.
Phishing and Social Engineering
AI-aided phishing campaigns blur the line between genuine and malicious communication, increasing the risk of falling victim to scams.
AI can craft highly convincing phishing emails and messages by analyzing the language and content patterns that are more likely to deceive users.
Here are Couple of Examples of Email Fraud

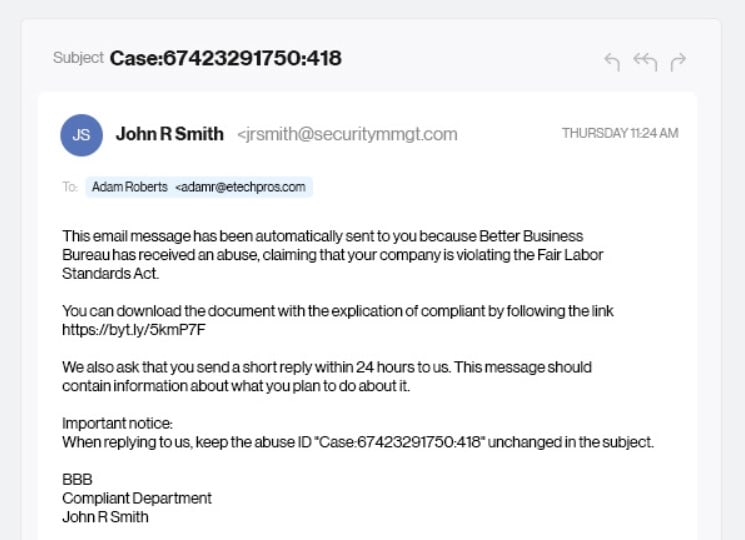
Notice the tone and sense of urgency. And the fact that it seems to come from a human makes it more challenging for people to identify and act on fraud.
AI-powered chatbots simulate human conversations and behavior and are being actively used to trick people into providing personal information, login credentials, and other sensitive information. AI-powered chatbots can also be used to assist in spreading malware.
Polymorphic Malware
Cybercriminals are using AI to create polymorphic malware that constantly changes its code and appearance, making it difficult for traditional antivirus solutions to detect.
Polymorphic malware is a shapeshifter that constantly evolves to evade detection, posing a significant challenge to cybersecurity professionals.
Password Cracking
AI algorithms can crack passwords more efficiently than ever before.
Cybercriminals can leverage AI to launch “dictionary attacks,” which is a focused and efficient method to gain unauthorized access to a system by trying an extremely large number of passwords from a pre-generated list of words, phrases, or commonly used passwords. But more that than, AI can automatically adjust the password cracking methods used, based on its understanding of the unique information and characteristics of the targeted organization and/or individuals.
Evading Detection
AI can be used to develop malware that actively evades detection by security tools. It can adapt its behavior to mimic legitimate processes, making it challenging to identify and mitigate.
The Dual Nature of AI
On the one hand, AI is a powerful ally to better protect digital assets and respond to threats, while on the other, it is a formidable weapon for cybercriminals, equipping them with powerful tools to carry out attacks more effectively.
AI has become a pivotal force in the ongoing battle between cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals.
Its ability to analyze vast datasets, identify anomalies, and automate responses has revolutionized threat detection and response. However, the same technology is being harnessed by malicious actors to carry out more sophisticated and damaging attacks.
Combat AI Cybercrimes
This year, NIST released the AI RMF 1.0 to help businesses determine the unique risks posed by AI, while helping to keep their businesses safe.
The NIST AI RMF provides organizations with a methodical and repeatable framework for developing a risk management program and assessing and managing various types of risks associated with both the use and development of AI, as well as the trustworthiness of such systems.
The NIST AI RMF 1.0 framework can be used to build a program of controls and oversight, Lyons explained, which then allows businesses to complete assessments against these controls and framework to determine the maturity of the program as well as how and where their program can be improved.
How does 360 Advanced help?
360 Advanced has a team of cybersecurity and compliance professionals who specialize in helping organizations and businesses implement the NIST AI RMF.
360 Advanced helps you become a market leader by becoming third-party assessed in the risk-based approach to using and/or developing AI capabilities.
“We can assist you in establishing a robust AI risk management program right from the start, preventing potential legal and ethical dilemmas and the need for expensive rework and adjustments down the road,” Lyons said.
Contact us to get started with your AI RMF 1.0 assessment.